Understanding The 7 Key Factors That Stabilize Negative Charge (And Ultimately, Basicity)
Like I wrote about in a previous post, it’s good – but not enough – to recognize partial charges and to figure out where they interact.
Since reactions involve processes that lead to the gain or loss of charges, understanding the factors that stabilize (or destabilize) charge have a tremendous impact on how likely a reaction is given to occur!
Let’s talk about negative charge today, which mostly means “anions” for our purposes but can broadly refer to any lone pair of electrons.
Table of Contents
- Understanding The Stability Of Negative Charge Helps Us Understand What Reactions Are Likely (And Not Likely) To Occur
- Factor #1: High Charge Densities Are Unstable
- Factor #2: As Electronegativity Increases Across The Periodic Table, So Does The Stability Of Negative Charge
- Factor #3: As Polarizability Increases Down The Periodic Table, So Does The Stability Of Negative Charge
- Factor #4: Resonance Stabilization Of Negative Charge
- Factor #5: Electron-Withdrawing Groups (Inductive Effects) Stabilize Negative Charge
- Increasing s-Character In The Hybridization Of An Atom Is Effectively Like Increasing Its Electronegativity
- A Special Case: Aromaticity
- “Basicity” Is Just Another Word For “Stability Of The Negative Charge”
1. Understanding The Stability Of Negative Charge Helps Us Understand What Reactions Are Likely (And Not Likely) To Occur
Let’s talk about a concrete example. For instance if a reaction leads to the formation of a very unstable negative charge, it’s unlikely to occur. But if it leads to the loss of a very unstable negative charge, it’s considerably more likely.
For instance, that’s why one of these reactions of methane is likely and the other is unlikely. These acid-base reactions are covered here, BTW.
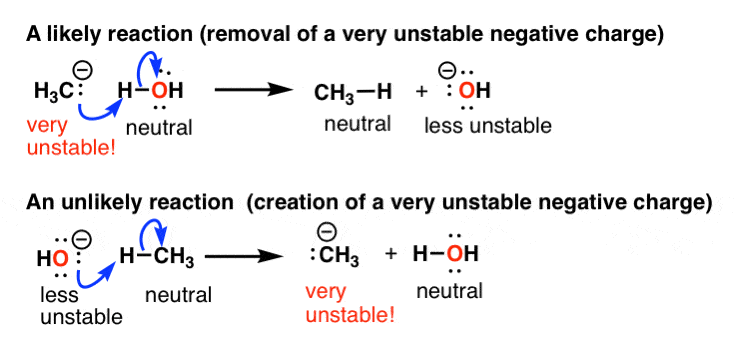
So what factors lead to the stabilization of negative charge? Two main things.
- negative charge is stabilized by adjacent positive charge (opposite charges attract!)
- negative charge tends to be less stable when it’s concentrated and more stable when it’s dispersed.
Think about that as you look at this list of seven factors that stabilize negative charge.
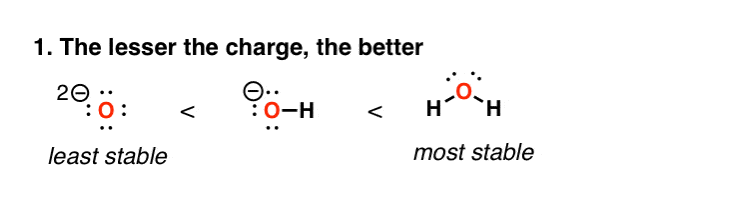
2. Factor #1: High Charge Densities Are Unstable
This one’s fairly straightforward to understand. High charge densities are unstable. So as we move from water to HO(–) to O(2-), we are getting progressively more unstable here. This is reflected in acidity tables; water (H2O) is far more likely to lose a proton to give HO(–) than HO(–) is likely to lose a proton to give O(2-)
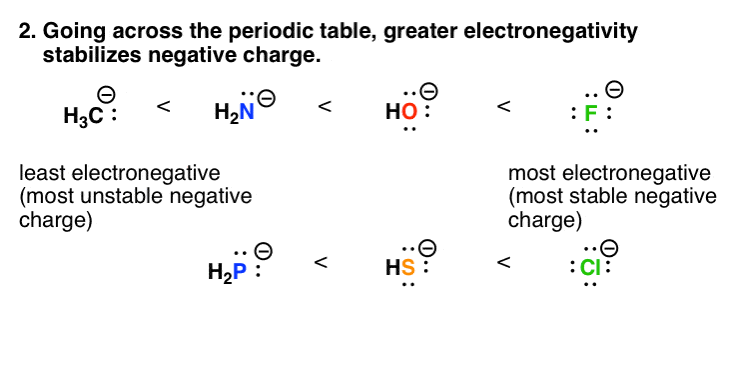
3. Factor #2: As Electronegativity Increases Across The Periodic Table, So Does The Stability Of Negative Charge
Electronegativity is a rough measure how effectively the positively charged nucleus of an atom can “pull” electrons toward it. (Opposite charges attract.)
Electronegativity increases as we go across the periodic table. So if you compare the anions going from C , N, O to F across the periodic table, the stability of the negative charge will increase. This is also reflected in acidity values.
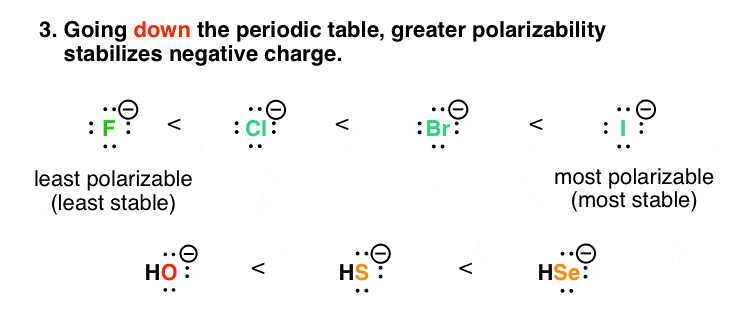
4. Factor #3: As Polarizability Increases Down The Periodic Table, So Does The Stability Of Negative Charge
Down the periodic table, it’s a little more helpful to think “dispersal of charge is good!” rather than “opposite charges attract”. Compare fluorine and iodine. The size of the fluorine ion (radius: 119 pm) is much smaller than iodine (radius: 206 pm). However, they both have a charge of negative 1.
Imagine two balls, each weighing one pound. But one is made of iron, and the other is made of rubber. Which ball is going to be smaller? The iron ball (smaller and harder – more dense) is like fluorine, and the rubber ball (larger and squishier) is like iodine. And a certain “squishiness” helps to stabilize charge, since it isn’t as concentrated over a small volume. That’s a way of expressing the greater polarizability of iodine.
Low charge densities are more stable!
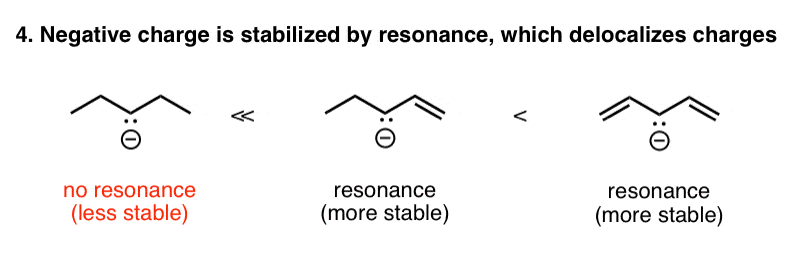
5. Factor #4: Resonance Stabilization Of Negative Charge
Along the same lines, a negative charge that is adjacent to one or more pi (π) bonds can disperse its negative charge over multiple atoms. We describe this phenomenon as “resonance“.
So in the example below, the negatively charged alkane on the left is much less stable than the adjacent negatively charged species, where the negative charge can be dispersed over multiple carbons through resonance. This is another example of how reducing charge density (or spreading it out) is a stabilizing influence.
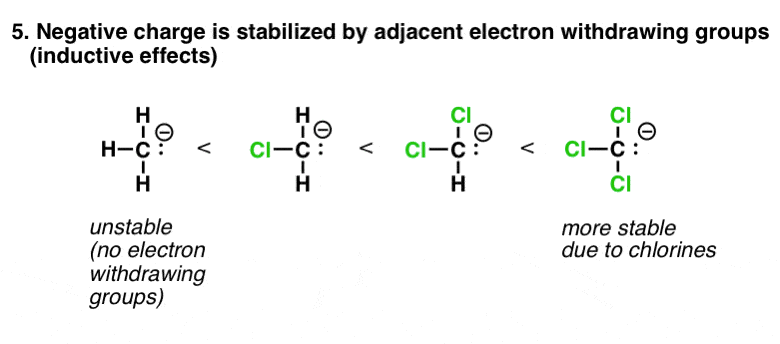
6. Factor #5: Electron-Withdrawing Groups (Inductive Effects) Stabilize Negative Charge
This one falls more into the auspices of “opposite charges attract”. A negative charge that is adjacent to an atom with electron withdrawing groups on it will be much more stable than an equivalent atom that is not. In the extreme case of CCl3(-), the resulting ion is many orders of magnitude more stable than H3C(-) itself. (This is the basis of the haloform reaction, by the way – see post).
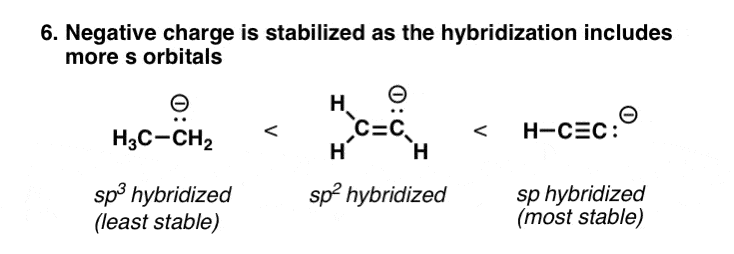
7. Increasing s-Character In The Hybridization Of An Atom Is Equivalent To Increasing Its Electronegativity
s orbitals are closer to the nucleus than p orbitals are. So electrons that are in s orbitals will be closer to the nucleus than electrons in p orbitals – and therefore, lower in energy (“opposite charges attract”). For this reason, electrons that are in sp orbitals are lower energy than sp2, which is lower energy than sp3, since they have greater s character (33% for sp2) than sp3 (25%). This makes the anions more stable, just as if it were on a more electronegative atom.
This is why terminal alkynes (pKa = 25) are much more acidic than alkenes and alkanes (pKa = 50)
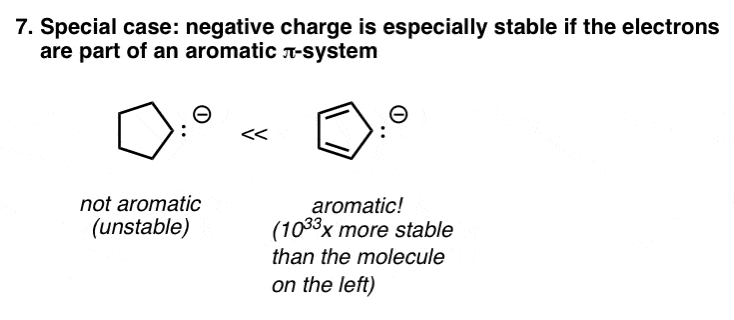
8. A Special Case: Aromaticity
This is a special case, covered in detail in organic chemistry 2 (peek ahead). Certain molecules possess a special stability – called aromaticity – that is enormously stabilizing, kind of like qualifying for a huge tax break from the government.
Certain negatively charged molecules – such as the cyclopentadienyl anion, pictured below – are aromatic, and therefore possess much greater stability than they would have otherwise.
9. “Basicity” Is Just Another Word For “Stability Of The Negative Charge”
Seven factors?!!! So how do we know which is most important?
That’s a great question! These trends can interact with each other in unpredictable ways, and it’s hard to judge which is most important.
Thankfully, there’s a concept you’ve probably already met for figuring out the stability of these species, which can be readily measured. It’s called basicity. These factors determine how stable a base will be!
The basicity of a species tells you about how stable its lone pair of electrons are.
How do we find a good measure of basicity? Simple. It’s in the pKa table, a collection of measurements that’s been compared to the table of hand strengths in poker.
Bottom line:
- Two factors to watch out for: opposite charges attract, and dispersal of charge.
- unstable anions will tend to be at the intial tails of arrows (form bonds).
- stable anions will tend to be at the final heads of arrows (likely to be leaving groups)
